Editors should consider screen reader users when using images. Screen reader users
include people who are blind, have low vision, or have cognitive disabilities. Pages
should provide effective text alternatives for screen readers in the form of alt text. When a screen reader encounters an image, it will attempt to read a text alternative.
Text alternatives are also important when images do not load. Users with cognitive
impairments may prefer to disable images from loading. Likewise, images may not load
when a user has a slow internet connection. In both cases, the browser will show the
image’s alt text.
Users with cognitive impairments, motion sensitivity, or seizure disorders may not
tolerate some kinds of images well. They can find moving, flashing, or automatically
animating images (including gifs) problematic.
Users with low vision often magnify the page. When magnified, images can appear pixelated
and hard to understand. Colorblind users benefit when all content, including images,
uses generous color contrast ratios.
Whenever a page presents images and other non-text content, it should present text
alternatives. These text alternatives provide the same information presented by the
image.
The most common form text alternative is alt text. alt text is a brief label contained in the HTML code for the image. Content editors can
generally provide alt text at the same time they upload images into websites. Screen readers read alt text aloud, and browsers pages alt text when images fails to load.
Long descriptions are lengthier amounts of text provided nearby the image, such as
in the next paragraph. Long descriptions are helpful when a brief alt text is not enough to convey information, such as in a complex chart or graph.
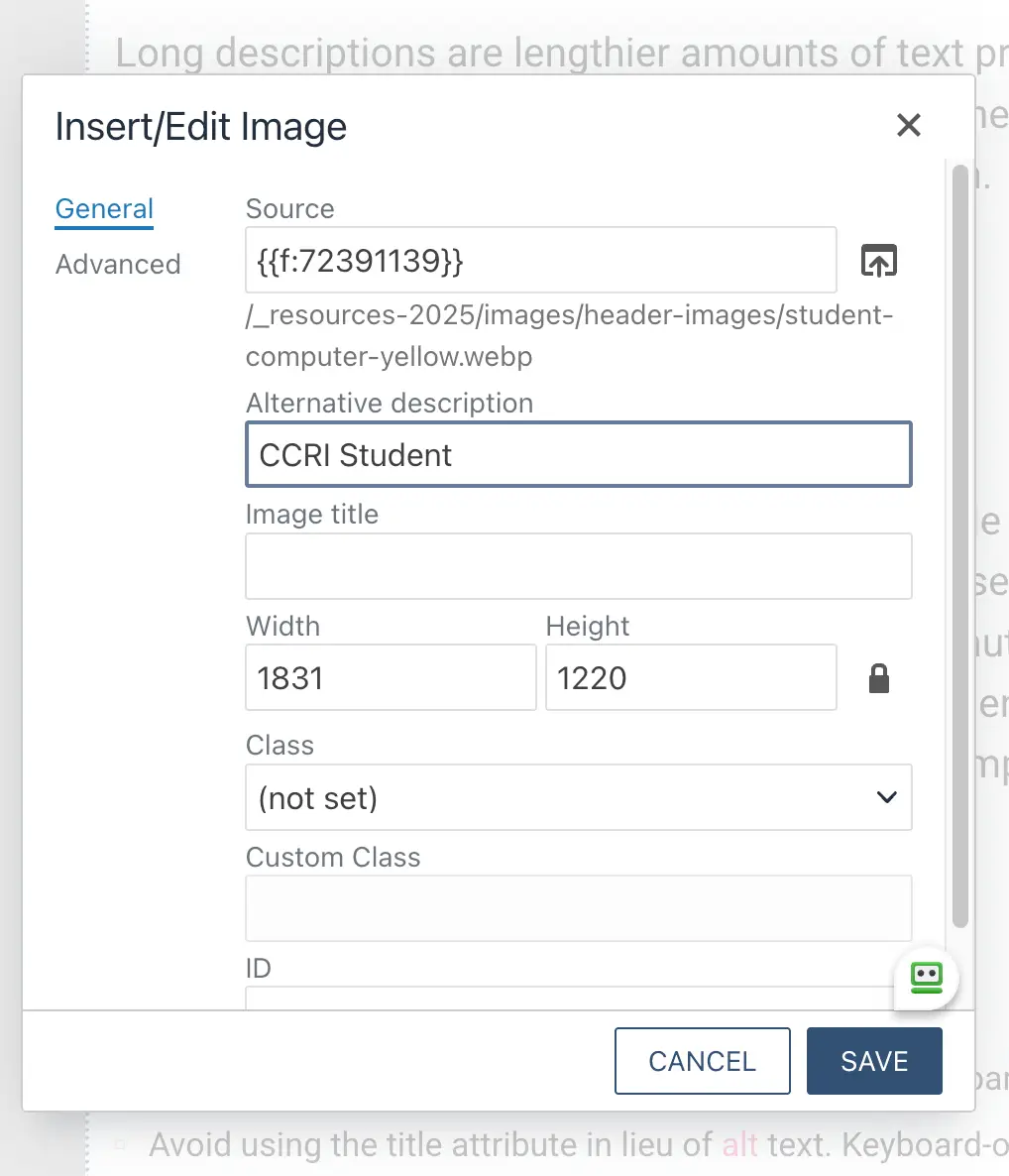
Understanding what makes good alt text is subtle and important. It should be brief: less than 250 characters. It should
convey the purpose of the image, not describe the image. When writing alt text, consider what details the author thought was most important. The same image
can have quite different alt text depending on its context. Consult the content editor slides at the top of the
page for more examples.
- Avoid “image of”, “photo of”, etc, unless the medium is particularly important.
- Avoid using the title attribute in lieu of
alt text. Keyboard-only users or mobile users may never see the title.
- Image links should describe the purpose of the link, and must never describe the image.
- Decorative images should have blank or empty
alt text
- Complex images, like charts or graphs, should have long description located near the
image. The image’s
alt text should describe where the close by image is.
- Posters, flyers, and the like must have the same information presented in nearby text/
- Provide color contrast and other design elements to help color blind users
In general, websites should avoid images of text. Images of text are best reserved
when a particular visual presentation is essential, such as a logo. If the image is
of a small amount of text, the alt text must match the text in the image exactly. If the image contains a considerable
amount of text, the text should also be elsewhere on the page.
In general, text in images should be a generous size to mitigate pixelation when zoomed.
A minimum size of 19px is a good rule of thumb, with larger being better. Text in
images should match color contrast ratio minimums. For text that is at least 24px
and normal weight or 19px and bold, use a contrast ratio that is at least 3:1. Ideally,
use a contrast ratio that is at least 4.5:1.