We wish to acknowledge Dr. Louis Zanella's generosity in giving us permission to
include material from his dissector in this web site. It is a wonderful
addition to this study tool and we are grateful to him.
A Regional Dissector
of the Cat, Louis J.
Zanella, Ed.D.,
1996
Chapter
1: Thorax, Shoulder and Neck
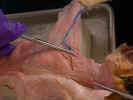
Skin the cranial left quarter of the cat by making a
midventral incision from the level of the ear to the level of the umbilicus.
Make a transverse incision to the left from the caudal end of the midventral
incision to the dorsal midline. Make a second transverse incision to the left
from the cranial end of the midventral incision, just caudal to the ear, to the
dorsal midline. Make a third transverse incision to the left from the midventral
incision down the forelimb to the wrist. Make a circular incision around the
wrist and reflect the skin to the dorsal midline.
Examine
the muscles on the dorsal surfaces. Clean the muscles to expose the directions
of the fibers. Identify and isolate each muscle using blunt dissection, freeing
each muscle from its origin to its insertion. Do not remove the muscles from
their attachments.
On the
dorsal surface identify the three divisions of the trapezius muscles. The spinotrapezius
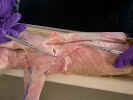
 muscle originates from the spinous process of the fourth through the twelfth
thoracic vertebrae and inserts on the spine of the scapula. The acromiotrapezius
muscle originates from the spinous process of the fourth through the twelfth
thoracic vertebrae and inserts on the spine of the scapula. The acromiotrapezius
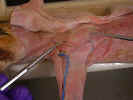
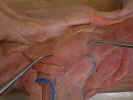 muscle lies cranial to the spinotrapezius and it arises from the spinous
processes of the cervical and the first four thoracic vertebrae. It inserts on
the spine and metacromion process of the scapula. The clavotrapezius
muscle lies cranial to the spinotrapezius and it arises from the spinous
processes of the cervical and the first four thoracic vertebrae. It inserts on
the spine and metacromion process of the scapula. The clavotrapezius
 muscle arises from the superior nuchal line of the skull and from the mid-dorsal
line of the neck to the spine of the axis and inserts on the clavicle.
muscle arises from the superior nuchal line of the skull and from the mid-dorsal
line of the neck to the spine of the axis and inserts on the clavicle.
Identify
the latissimus dorsi 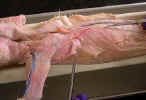
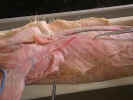 and omotransversarius muscles
and omotransversarius muscles 


 (levator scapulae ventralis). Separate the spinotrapezius
from the underlying latissimus dorsi muscle. The latissimus dorsi
muscle originates from the thoracolumbar fascia over the spinous processes of
the fifth thoracic through the sixth lumbar vertebrae and inserts on the
proximal end of the humerus. Isolate the latissimus dorsi muscle.
(levator scapulae ventralis). Separate the spinotrapezius
from the underlying latissimus dorsi muscle. The latissimus dorsi
muscle originates from the thoracolumbar fascia over the spinous processes of
the fifth thoracic through the sixth lumbar vertebrae and inserts on the
proximal end of the humerus. Isolate the latissimus dorsi muscle.
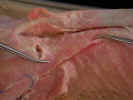
Transect the latissimus dorsi muscle two inches from its insertion on the
humerus and reflect it to its attachments. Clean and observe the thoracodorsal
artery 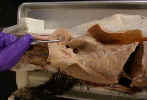
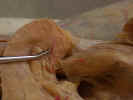 and nerve
and nerve 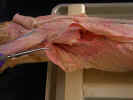
 on the inner surface of the latissimus dorsi at its
humeral end.
on the inner surface of the latissimus dorsi at its
humeral end.
Identify
the three divisions of the deltoid muscle. The clavobrachialis
muscle 
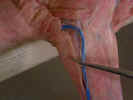
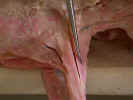 (clavodeltoid) arises from the clavicle and inserts on the
ulna. The acromiodeltoid muscle
(clavodeltoid) arises from the clavicle and inserts on the
ulna. The acromiodeltoid muscle 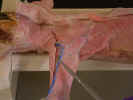
 arises from the metacromion process of the scapula deep to the omotransversarius
and inserts on the proximal end of the humerus. The spinodeltoid muscle
arises from the metacromion process of the scapula deep to the omotransversarius
and inserts on the proximal end of the humerus. The spinodeltoid muscle
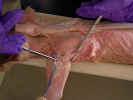
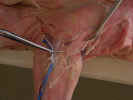 arises from the spine of the scapula and inserts on the proximal end of the
humerus.
arises from the spine of the scapula and inserts on the proximal end of the
humerus.
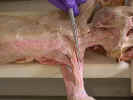
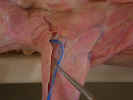
Observe
the cephalic vein 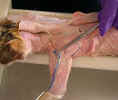
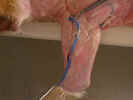 caudal to the clavobrachialis. Dissect the caudal margin of the clavobrachialis
and Isolate the axillary nerve
caudal to the clavobrachialis. Dissect the caudal margin of the clavobrachialis
and Isolate the axillary nerve 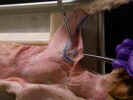
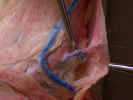 as it enters the deep surface of the clavobrachialis just distal to the
clavicle. Isolate the acromiodeltoid and spinodeltoid muscles as
far as possible.
as it enters the deep surface of the clavobrachialis just distal to the
clavicle. Isolate the acromiodeltoid and spinodeltoid muscles as
far as possible.
On the
ventral surface, identify the superficial pectoral muscles. The pectoantebrachialis
muscle 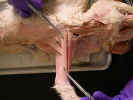
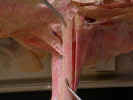 originates from the manubrium. Isolate this muscle from the pectoralis
major
originates from the manubrium. Isolate this muscle from the pectoralis
major 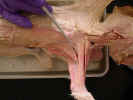
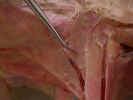
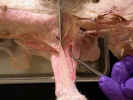
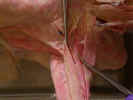
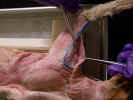
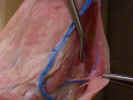 and trace it to its insertion on the ulna. Transect this muscle and reflect it
to its attachments. The pectoralis major muscle has its origin on the
first three sternebrae and inserts on the proximal two thirds of the humerus.
and trace it to its insertion on the ulna. Transect this muscle and reflect it
to its attachments. The pectoralis major muscle has its origin on the
first three sternebrae and inserts on the proximal two thirds of the humerus.
The deep
pectoral muscle consists of the pectoralis minor 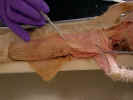 and the xiphihumeralis
and the xiphihumeralis 
 .
The pectoralis minor muscle arises from the body of the sternum and
inserts on the proximal half of the humerus. The xiphihumeralis muscle
arises from the xiphoid process and passes deep to the pectoralis minor
to insert on the proximal end of the humerus. Separate the pectoral muscles so
that their attachments can be seen.
.
The pectoralis minor muscle arises from the body of the sternum and
inserts on the proximal half of the humerus. The xiphihumeralis muscle
arises from the xiphoid process and passes deep to the pectoralis minor
to insert on the proximal end of the humerus. Separate the pectoral muscles so
that their attachments can be seen.
The clavobrachialis
muscle lies cranial to the pectoral muscles. It arises from the clavicle and
inserts on the ulna. Palpate the clavicle located medial to the greatest
tubercle of the humerus. The clavotrapezius muscle arises from the
superior nuchal line of the skull and from the mid-dorsal line of the neck to
the caudal end of the axis and inserts on the clavicle. Dissect the cranial
margin of the clavobrachialis and the clavotrapezius.
Displace
the pectoral muscles cranially and observe the fan shaped serratus
ventralis muscle 


 .
The serratus ventralis muscle arises from the last five cervical
vertebrae and the first nine ribs and inserts on the vertebral border of the
scapula. Identify the long thoracic nerve
.
The serratus ventralis muscle arises from the last five cervical
vertebrae and the first nine ribs and inserts on the vertebral border of the
scapula. Identify the long thoracic nerve
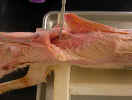
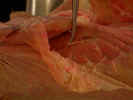 along its lateral surface.
along its lateral surface.
Find
the three scaleni muscles on the thoracic wall deep to the pectorals.
They arise from the cervical vertebrae and insert on ribs one through nine.
Medial to the scaleni identify the small rectus thoracis muscle and the cranial
portions of the rectus abdominis muscle. The rectus thoracis arises from the
sternum and inserts on the first rib.
In the
neck, observe the external jugular vein 
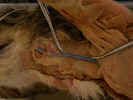 on the medial border of the clavotrapezius
muscle as it crosses the sternomastoid muscle superficially.
Dissect the medial border of the clavotrapezius muscle and Isolate the sternomastoid
muscle.
on the medial border of the clavotrapezius
muscle as it crosses the sternomastoid muscle superficially.
Dissect the medial border of the clavotrapezius muscle and Isolate the sternomastoid
muscle.
The sternomastoid
muscle 
 arises from the manubrium of the sternum and inserts on the mastoid process and
the nuchal line of the skull. Identify the cleidomastoid muscle deep to
the sternomastoid and the clavotrapezius. It arises from the
clavicle and inserts on the mastoid process of the skull. The omotransversarius
muscle may be seen dorsal to the cleidomastoid.
arises from the manubrium of the sternum and inserts on the mastoid process and
the nuchal line of the skull. Identify the cleidomastoid muscle deep to
the sternomastoid and the clavotrapezius. It arises from the
clavicle and inserts on the mastoid process of the skull. The omotransversarius
muscle may be seen dorsal to the cleidomastoid.
Locate
the sternohyoid muscle 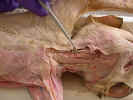
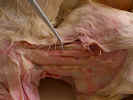 originating from the manubrium and inserting on the hyoid bone in the ventral
midline of the neck. The sternothyroid muscle
originating from the manubrium and inserting on the hyoid bone in the ventral
midline of the neck. The sternothyroid muscle 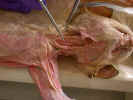
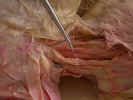 is located deep and lateral to the sternohyoid. It originates on
the manubrium and inserts on the thyroid cartilage of the larynx. Isolate
these muscles from their origin to their insertion.
is located deep and lateral to the sternohyoid. It originates on
the manubrium and inserts on the thyroid cartilage of the larynx. Isolate
these muscles from their origin to their insertion.
Last Updated: 9/9/24

 muscle originates from the spinous process of the fourth through the twelfth
thoracic vertebrae and inserts on the spine of the scapula. The acromiotrapezius
muscle originates from the spinous process of the fourth through the twelfth
thoracic vertebrae and inserts on the spine of the scapula. The acromiotrapezius

 muscle lies cranial to the spinotrapezius and it arises from the spinous
processes of the cervical and the first four thoracic vertebrae. It inserts on
the spine and metacromion process of the scapula. The clavotrapezius
muscle lies cranial to the spinotrapezius and it arises from the spinous
processes of the cervical and the first four thoracic vertebrae. It inserts on
the spine and metacromion process of the scapula. The clavotrapezius

 muscle arises from the superior nuchal line of the skull and from the mid-dorsal
line of the neck to the spine of the axis and inserts on the clavicle.
muscle arises from the superior nuchal line of the skull and from the mid-dorsal
line of the neck to the spine of the axis and inserts on the clavicle. 






 and nerve
and nerve 
 on the inner surface of the latissimus dorsi at its
humeral end.
on the inner surface of the latissimus dorsi at its
humeral end.




































